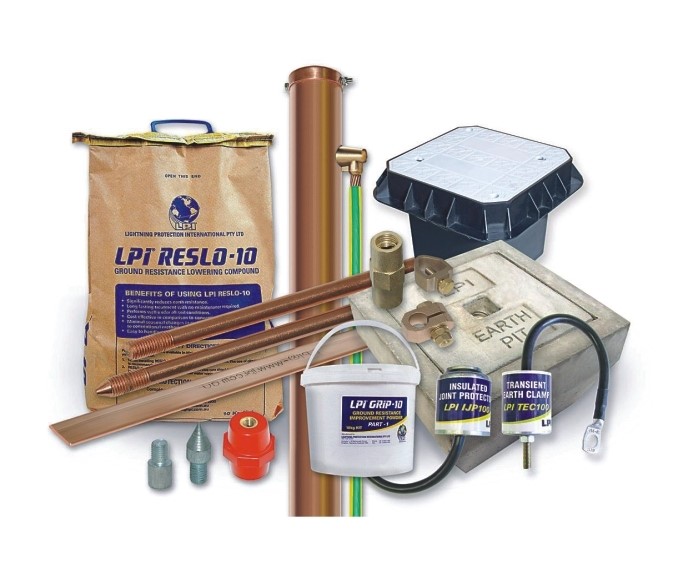
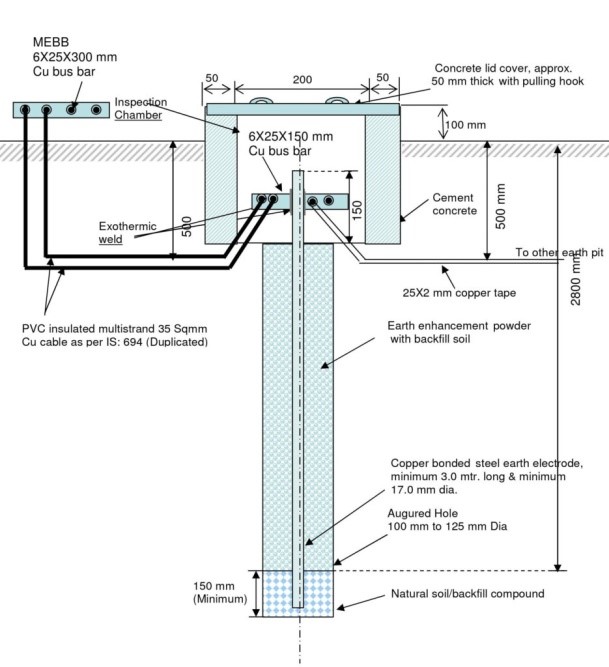
Earth Pit
Pipe Earthing
Pipe Earthing is one of the most common earthing techniques. The pipe earthing uses a galvanized iron (GI) pipe, and the dimension of the GI pipe used for a structure depend mainly on the magnitude of possible current and the soil type.
The dimension of the pipe is usually 40mm (1.5in) diameter and 2.5m (9ft) length for ordinary soil and greater for dry and rocky soil as the soil resistivity is higher in such cases.
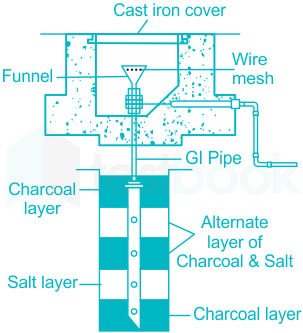

Chemical Earthing
Chemical Earthing is an advanced method of earthing that differs significantly from traditional earthing techniques. In conventional earthing, materials like charcoal and salt are commonly used to maintain moisture around the earthing electrode, which helps to conduct electricity effectively into the ground. However, these materials can degrade over time, leading to increased resistance and the need for regular maintenance.
Chemical Earthing, often referred to as Maintenance-Free Earthing, offers a more efficient and long-lasting alternative. Instead of relying on charcoal and salt, Chemical Earthing uses specialized ground-enhancing materials. These materials, such as a fill compound, are designed to surround the earthing electrode. The fill compound is a highly conductive material that does not degrade easily over time. It ensures a consistent and low-resistance path for electrical currents to dissipate into the ground.